
In News
Implementing Self Trading Prevention
On Tuesday, January 20th, we are introducing our new self trading prevention mechanism
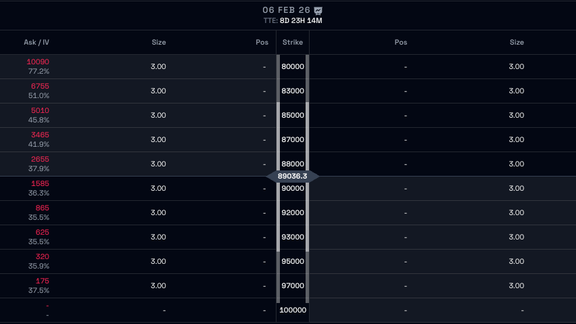
In News
Futures Rolls Fee Change
As of January 6th, 2026, we are changing how we charge fees on Futures Rolls
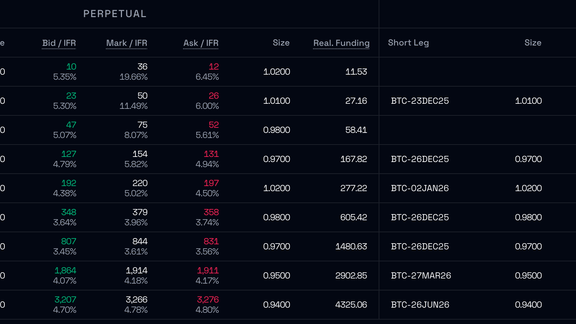

In Guides
How to connect to our API using Python
We show you step-by-step how to connect to and use our API.

In News
Minimum Order Size and Volume Tick Size Changes on 25th of November.
On Tuesday, November 25th, we are making changes to our minimum order size and volume tick size.

In Education
Options
An option is a contract that gives the buyer the right, not the obligation, to trade an underlying at a preset strike on or before a stated expiry. A call conveys the right to buy. A put conveys the right to sell. Buyers pay an upfront premium and can exit before expiry by selling the option back to the market. Options are used to seek upside with less capital, hedge downside, or monetize views on volatility.
In Education
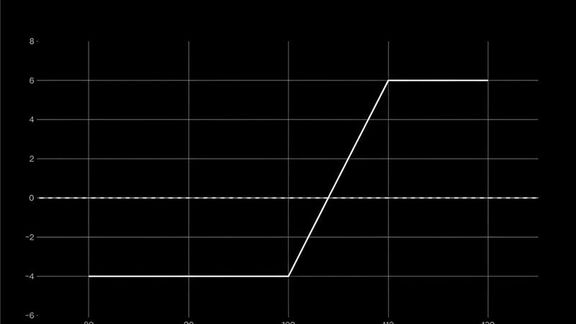
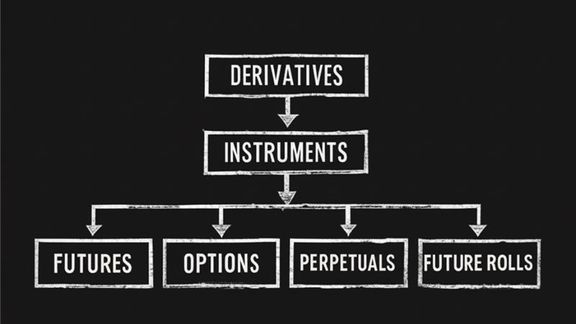
Derivatives Basics
Derivatives move risk without moving the asset. Dated futures have cost of carry, perps have funding, options have convexity. These create a basis between derivative price and spot. You can trade the curve with calendars and future rolls to shift exposure across expiries while keeping net delta near zero.
In Education
Futures & Perpetuals
Traditional futures are standardized legal contracts to buy or sell an underlying asset at a preset price. Every traditional future has a set expiration date, upon which the contract is settled and ceases. Because futures have a finite lifespan, their price is governed by the market’s forecast of the asset value at the future’s expiration date. Taking into accounts factors like interest rates and storage costs (‘cost of carry’).